The ACME service is used to automate the process of issuing X.509 (PKIX) certificates using the ACME protocol, as defined in RFC 8555.
The ACME protocol is supported by many standard clients available in most operating systems for automated issuing, renewal and revocation of certificates. For example, the certbot ACME client can be used to automate handling of TLS web server certificates for common HTTP servers, such as Apache and Nginx. For more information, see ACME Client Implementations.
Many critical services and servers are already equipped with certificates proving their identity in a secure way, but lack the automation for example to renew certificates when the existing ones are expiring. Critical services often stop due to the fact that their certificate expire and manual processes are involved. The automation that comes with ACME enables universal encryption on the Internet.
ACME is also readily available in many server applications and devices that need X.509 certificates, making it easier to automatically provision certificates. Many devices, such as servers, printers and NAS (Network-attached storage) devices, also come with support for ACME.
The ACME service in Protocol Gateway (PGWY) supports both public-facing internet ACME account creation and ACME account creation where a pre-registered secret key must be shared beforehand.
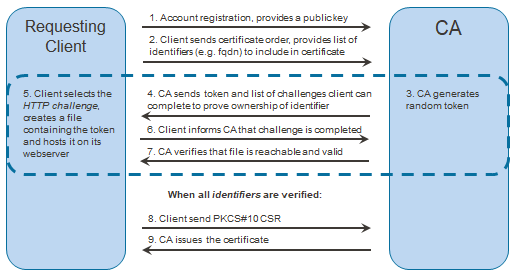
ACME protocol flowchart
The diagram illustrates how an ACME client can obtain a certificate without any human interaction. In the dashed region, the client proves ownership of the domain using an HTTP-based challenge. There are other challenge methods available for ACME, Certificate Manager also implements the DNS challenge. Step 1 is optional, clients can be pre-registered in Certificate Manager – but then the clients needs to be manually provisioned.